
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
HKUST seeks to be a regional leader in prioritizing clean energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and expanding renewable energy infrastructure. We aim to be a global leader in energy research and development, influencing policies and strategies while setting an example for sustainable development in Hong Kong and beyond. Through our campus operations and community engagement initiatives, HKUST plays an active role in renewable energy adoption and carbon emissions reduction.
Curriculum
51 related courses were offered in the 2023-24 academic year.
Research
According to Science Direct, from 2020 to 2024, HKUST published 1831 research papers addressing SDG 7.
34.84% of them are in the top 10% cite score and 75.5% are internationally co-authored.
Research Highlights
HKUST Researchers Enhance Performance of Eco-Friendly Cooling Applications by Developing Sustainable Strategy to Manipulate Interfacial Heat Transfer
Researchers have developed a sustainable and controllable strategy to manipulate interfacial heat transfer. By engineering specialized molecular structures, the team achieved a sevenfold increase in thermal performance — paving the way for improving performance of eco-friendly cooling in various applications such as electronics, buildings and solar panels. This breakthrough in thermal management could significantly reduce energy consumption across multiple industries, supporting the transition to greener technologies and sustainable energy solutions.
Prof. ZHOU Yanguang (second right), Assistant Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at HKUST, and his PhD students FAN Hongzhao (first left), WANG Guang (second left) and LI Jiawang (first right)
Passive Radiative Cooling For Solar PV Frames + Cooling Tower Water Tank
The project aims to demonstrate two opportunities by improving efficiency and generating energy savings, leveraging radiative cooling technology to align with HKUST's net-zero target. In the cooling system efficiency sector, applying radiative cooling paint to the water tank for cooling towers can remove heat from the water inside and maintain a lower temperature, extracting more heat from the indoor environment in each cycle and consuming less energy during the cooling process. In the solar panel power conversion efficiency sector, radiative cooling can support heat reduction of solar panels and solar panel frames, thus allowing HKUST to produce more renewable energy with the same number of solar panels.

Smart Building Integrated Photovoltaic Systems Toward Zero Energy HKUST Campuses
The project aims to investigate the solar energy harvesting potential on opaque façade areas and apply more advanced clean energy systems like tailored colored façade integrated photovoltaic (FIPV) on campus buildings. It will also improve energy efficiency by passively cooling the systems, using radiative cooling and self-cleaning coatings techniques.

Low-Carbon Elastocaloric Fridges And Air Conditioners For Sustainable And Smart HKUST
The project suggests a solid-state elastocaloric refrigeration technology that is zero-GHG-refrigerant and 100% recyclable based on phase-transition shape memory alloys, avoiding GHG usage and having high cooling power and efficiency. The project aims to promote HKUST to be the first sustainable campus that uses energy-efficient zero-GHG-refrigerant elastocaloric cooling technology.

A Multi-Year Campus-Level Smart Meter Database
With the growing need for precise campus electricity management, understanding load patterns is crucial for improving energy efficiency and optimizing energy use. However, detailed electricity load data for campus buildings and their internal equipment is often lacking, hindering research. In light of this, a team of researchers published to introduce an energy consumption monitoring dataset from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) campus in Hong Kong, comprising data from over 1400 meters across more than 20 buildings and collected over two and a half years. Using the Brick Schema curation strategy, raw data was curated into a research-ready format. This dataset supports various research tasks, including load pattern recognition, fault detection, demand response strategies, and load forecasting.
Policy
HKUST Net-Zero Building Standards
HKUST is committed to improving the energy efficiency of its new buildings as well as renovation projects through the implementation of newly updated HKUST Net-Zero Building Standards. The requirements outlined include anticipating future energy needs, maximizing metering and monitoring capabilities while keeping a flexible design to accommodate for future new sustainable technologies.
Collaboration
HKUST X SOCAM Joint R&D Project Visit: BIPV for Smart Low-carbon Mic Public Housing
HKUST promotes renewable energy adoption beyond its campus through various initiatives. The university partners with industry and government on transformative projects like the HKUST X SOCAM Joint R&D Project on "BIPV for Smart Low-carbon MiC Public Housing". This project, led by Prof. Xiang Changying, represents Hong Kong's first solar-powered modular housing solution featuring smart monitoring and self-cooling surfaces. Through demonstrating scalable clean energy applications and engaging stakeholders through policy dialogues and public education, HKUST accelerates sustainable urban development while advancing affordable clean energy.
HKUST's industry collaboration with SINO
The partnership between HKUST and Sino Land Company Limited, as outlined in the evidence webpage, exemplifies this commitment to helping local industry enhance energy efficiency. HKUST researchers collaborated with Sino Land for a year to establish science-based targets and develop a comprehensive Decarbonisation Blueprint. This joint effort enabled the property developer to set specific carbon reduction goals, implement climate risk assessments, and pursue net zero carbon emissions by 2050. Through this collaboration, HKUST successfully transformed its research on decarbonisation and carbon reduction into practical solutions for the building industry, striving for improved energy efficiency and sustainability.
SCMP News: HKUST's support in Emissions Calculation Tool Development
HKUST actively supports the government's initiatives in clean energy and energy-efficient technology policy development. A prime example of this collaboration is HKUST's involvement in creating greenhouse gas emissions calculation and estimation tools, launched in partnership with a cross-agency green finance body led by Hong Kong's financial regulators. These tools, developed with HKUST's expertise, directly contribute to the city's sustainability efforts by enabling companies, especially SMEs, to accurately measure and report their carbon emissions as required by the government. By providing accessible means for emissions calculation, HKUST bridges the gap between energy policy objectives and practical implementation, enabling more informed decision and supporting Hong Kong's transition to a sustainable, energy-efficient economy.
Community Engagement
SSC x Civic Exchange Sustainability Tour
HKUST's collaboration with Civic Exchange, welcoming a group of local high school students to campus to share sustainability initiatives. Energy-efficient projects were presented, including the application of passive radiative cooling technology to enhance solar PV efficiency and a green parking system powered by Edge cameras for EV drivers and carpoolers.

Operations
Electric Vehicles Charging Upgrades
To support the growing adoption of electric vehicles, HKUST has installed EV charging stations for 300 parking spaces in its staff housing areas, providing convenient access to medium-speed charging capabilities.
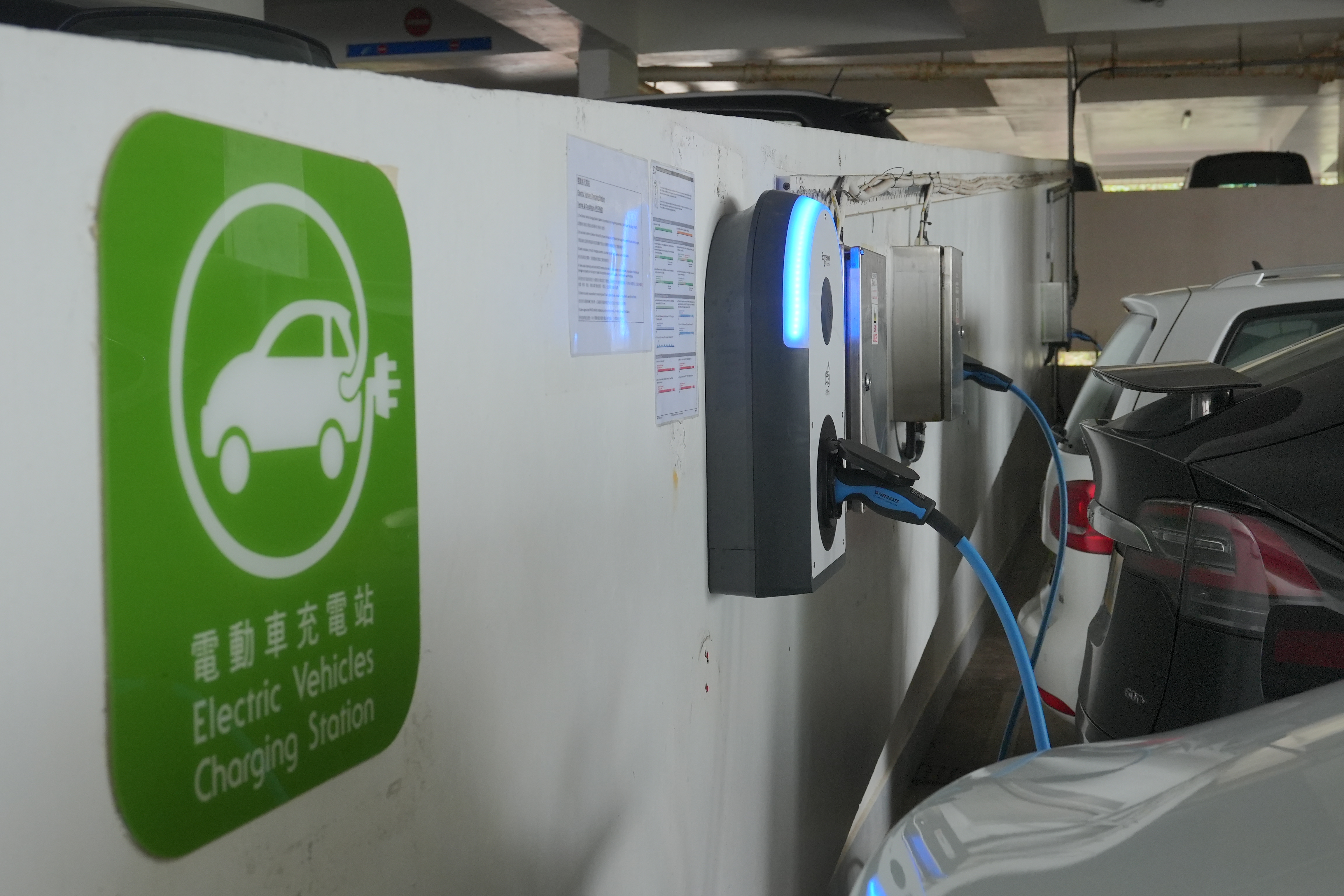

Newly installed Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Lighting Upgrade
Lighting upgrades have also been a major focus, with 5,842 light fixtures across campus now replaced with LED technology. These LED lights not only consume less energy but also integrate occupancy sensors in stairwells and corridors, automatically turning off when the spaces are unoccupied. This has led to an average 60% reduction in lighting-related energy use
Lift Modernization with Regenerative Drivers
As part of a 10-year plan, lifts L17 and L18 at the Main Academic Building, L7 and L8 at Hall 2, and L8 at SSQ Tower 1 were modernized this year with the implementation of an energy regenerative drive system, resulting in approximately 30% energy savings for lifts compared to non-regenerative counterparts.
Remodelling of Laboratory Virtual Stack Fan
The laboratory exhaust system on the roof of the Main Academic Building supports the operation of laboratories and their fume hoods. These fans operate continuously throughout the year, consuming significant energy. Previously, these fume hoods were upgraded to low-flow types with auto sash, but the existing exhaust system cannot operate stably under reduced demand and unnecessarily operates at higher speeds.
To address these issues and enhance reliability, safety, and energy efficiency, this project will remodel and optimize the laboratory exhaust system on the main campus.
The main contract is set to be tendered at the end of 2023, with expected completion by the second quarter of 2025. The annual energy savings are estimated to be around 500,000 kWh.